Underwater Acoustic and Magneto-inductive Communications
Underwater communication inspires researchers in many unique ways. The low speed of sound in water, different attenuation characteristics and time varying multi-path fading make use of regular communication methods impractical. However, underwater communication is not without advantages. Due to the large heat capacity of water, underwater communication units need not be cooled externally, water does that already. Taking such constraints and advantages into consideration, one must design a totally new communication system.
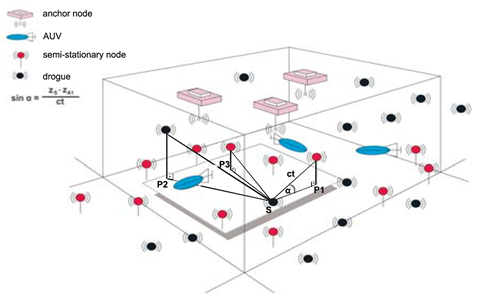
In order to exploit the advantages and overcome the difficulties communication via magnetic induction is suggested, which is one of the main focuses of our studies. Other than communication, localization of underwater objects is also an open problem. Such a problem is especially hard, as it is impossible to use Global Positioning System. Note that localization is a specific application of communication, which may be solved via similar approaches.