Mobile Ad Hoc beyond-Line-of-Sight (b-LoS) Networks
|| Funded by: Lockheed Martin || Period: November 2012 - November 2015 || Amount: $641.376 |
 |
Evaporation ducts, the layer in which rapid decrease in the refractive index occurs, can be used as communication medium in maritime and coastal environments for b-LoS communications. Since the propagating signals at microwave frequencies are trapped between ducting layer and sea surface due to the rapid change in the refractive index, the signal spreading through atmosphere becomes considerably less. As a result, the signals can travel over-the-horizon and this effect makes ducting layer a promising alternative for b-LoS communications.
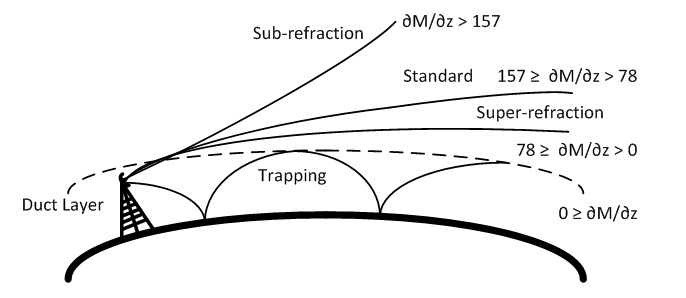
On the other hand, ducting layer forms lossy waveguide and introduces severe multipath effect due to reflection from rough sea surface and evaporation duct. Therefore, we will develop channel model for evaporation duct based b-LoS communications. In addition, advanced communication techniques will be introduced in order to improve the system against multipath effect and ad hoc networking will be utilized to both improve communication system against multipath effect and provide reliable high rate communication.